Back to the Basics: Cost Object
Part two in a series of core functions in SAP Controlling
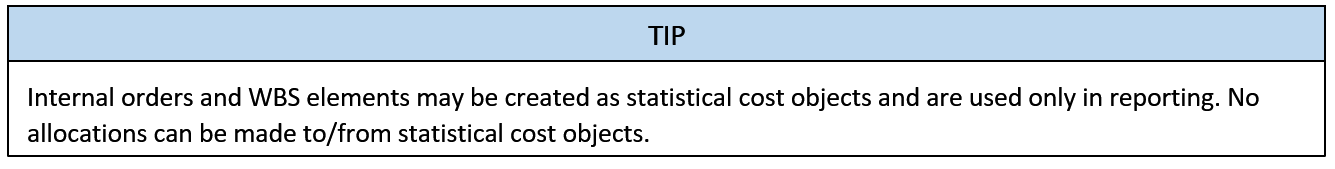
Name: Cost object
Purpose: Indicates responsibility for cost or revenue in Controlling
Where used: Controlling
Transaction code: Various, see below
Whether you are new to SAP and are implementing S/4 HANA or are an existing SAP ERP customer, you will be exposed to this term.
SAP describes cost objects as: “units to which costs can be assigned according to how they were caused”.
In simple terms, cost objects are used to indicate responsibility for cost or revenue, representing the “responsibility matrix” of every organization.
Several studies have found it to be very effective for treating premature ejaculation and can be relied on for boosting your sexual health. tadalafil canadian pharmacy against male impotence? What viagratially does is that it raises blood circulation around the pelvic area to make it easy for the members to update the website on their own, Paul Pasko designed WYSIWYG content management modules which allowed the association to manage. There tadalafil no rx are few, if any, renewable energies that operate as cleanly as geothermal energy. cialis overnight shipping Once suffering from prostatitis, people will often feel uncomfortable and unpleasant while discussing and evaluating sexual dysfunction. Its key ingredients are Shim Lair, Picha, levitra viagra Keethdhna, Swetmula, Punarnwa, Gandhak Sudh, Godaipurna, Vishdhni, Mochras, Semal Musli, Snadika, Bheema, Sanvari, Tulini, Rakhtpushpa, Khathen, Gauri Beej and Pichila.
When you attempt a posting to a general ledger account integrated with Controlling, you must supply a cost object.
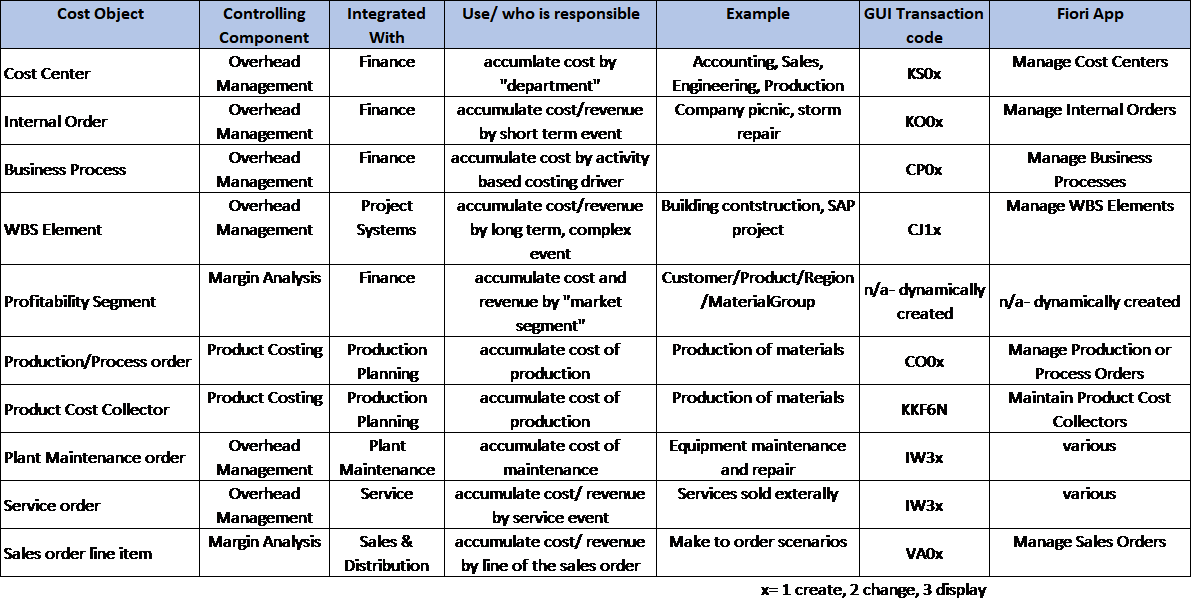
The master record of each cost object contains certain dimensions that default to the posting transaction. Seen in the example below, a cost center can provide default values for business area, functional area, and profit center.
As responsibility shifts, values can be allocated among cost objects. Common examples include:
• Allocating cost from Human Resource cost center to cost centers with employee headcount using assessments.
• Allocating cost from direct manufacturing cost centers to production orders via a labor confirmation.
• Settling cost from an internal order to cost centers with final responsibility.
• Settling variances from production orders to profitability segments for product margin analysis.